As you can see in this picture, brownian motion is the constant and random motion of small solid particles.
According to the Kinetic Particle theroy, all matter is made up of discrete particles which are in constant random motion.
This can be shown by observing smoke particles under a microscope. When heat is supplied the smoke particles start to move more vigorously constantly and randomly.
Einstein said that the random motion of the smoke particles was the result of being hit by unseen fast air molecules.
Diffusion is the random motion of particles from a region of high concentration to lower concentration.
For example, if a building caught fire, you are able to smell smoke from a distance away. This is because the smoke particles travelled from the building to your nose. The spreading of molecules on their own accord without external aid is called diffusion.
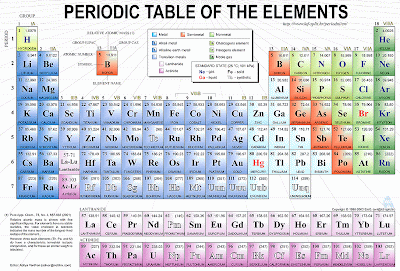
Here is a periodic table of elements.
What is an element?
And element is a basic building block of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any known chemical methods. The elements in the periodic table are classified according to their properties. As you look at the periodic table from left to right, you can see a gradual change from metallic elements to non metallic ones.

Compounds are substances that contain 2 or more elements joined together by a chemical reaction. A compound has different properties from its elements.
<--- These are examples of compounds.
The main component of wood is cellulose, which has the formula (C6H10O5)n The "n" is a variable. As cellulose is chemically joined by more than 2 elements, its a compound.
Process of making magnesium oxide. (oxygen + magnesium)
Mixture
In a misture of elements, the atoms of the elements are not chemically combined. The above picture shows a mixtureof table salt and sand. A mixture does not have a fiexed composition. The percentage of each substance in a mixture is not always the same.
Solutions
All solutions are mixtures consisting of a solvent (a substance that the soltute dissolves in) and a solute (the substance that dissolves). A solution is homogenous when the colour, density, appearance,
other physical and chemical properties are the same in every
part of the solution and light is able to pass though the solution.
A solution is hetrogenous when the insouluble particles are big enough to prevent light from passing through. This is called a suspension.
Seperation techniques
Different types of methods to separate constituents of a mixutre based on its properties:
- Filtration
- Evaporation to dryness
- Cystallizaton
- Seperating funnel
- Distillation and Fractional distillation
- Chromatography
- Magnetic attraction
Filtration
Filtration is a simple method to separate a solid from a liquid.
Evaporation to dryness
Evaporation to dryness is the evaporation of the solvent to obtain the solute. In evaporation to dryness, any soluble impirities will be deposited along with the required solid so it is unable to separate a pure substance from its impure form.
Crystallisation
Crytallisation is the process of heating the solvent until most of the solvent evaporated, then letting the solvent cool. After a while, the cooled solution is poured off to obtain the solid crystals.
Magnetic Attraction
By using magnetic attraction, you can seperate magnetic objects from non-magnetic objects.
Distillation
Distillation is used to purify liquids. It is used to obtain a pure solvent from a solution of a solute.
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is used to separate a mixture of miscible liquids using a fractional column.
Fractional distillation can also be used to obtaing pure oxygen and nitrogen from the air.
Separating Funnel
A separating funnel is used to separate mixtures that contain liquids which are not miscible. The tap is opened so that the lower layer of liquid runs out first into a beaker. The tap is closed when the last drop of the liquid leaves the funnel. The tap is opened again to run the upper layer of liquid into another beaker.
ChromatographyChromatography is the method of separating and identifying mixtures. There are many types of chromatography such as paper chromataography. The most commonly used solvent for paper chromatography is ethanol.
Chromatography can also be used to separate and indentify colourlesss substances using a locating agent. A locating agent reacts with substances to produce a coloured product.
Reverse Osmosis
In this process, a semi-permeable membrane is used. Unlike normal osomosis, in reverse osmosis
pressure is applied on one side of the membrane , forcing water molecules to passs throught the membrane, leaving behind the undesirable substances like virus. Clean water is obtained on the other side of the membrane.
Diffusion and Osmosis
Lets recap on diffusion: Diffusion is the net movement of atoms or molecules from a region where they are at a higher concentraion to a region where they are at a lower concentration.
Diffusion continues until the particles are uniformly distributed throughout the system.
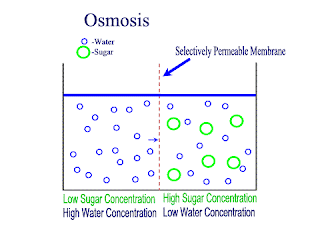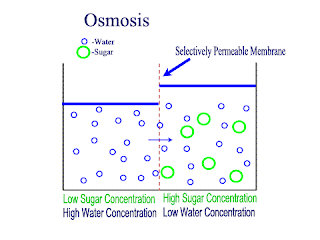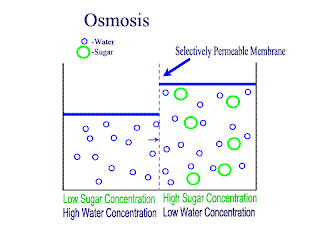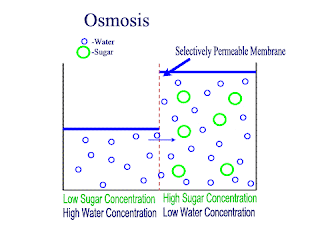
Osmosis
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules throught a partially permeable membrane, from a rgion of higher concentration of water molecules to a region of lower concentration of water molecules. Similar to diffusion, osmosis continues until the water concentraion is uniformly distributed between 2 solutions.
There are 3 types of solutions:- Isotonic solution (equal water concentration)
- Hypotonic solution ( higher concentration of water; lower concentration of solute)
- Hypertonic solution (lower concentration of water; hight concentration of solute)
CELLS (here comes my fav topic!!!)
Cells are the basic unit of life. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A human being like us is made up of millions of cells whereas living things like amoeba only have one cell. Thus amoeba is a unicellular organsim and a human is a multi-cellular organism.
An Euglena is a unicellular organism.

Whereas a human being, is a multicellular organism.
Animal cell
Plant cell
The main difference between a typical plant cell and a typical animal cell is that a plant cell has chloroplasts and a cell wall but an animal cell does not.
 Different cells of the same type work together to form tissues. Different tissues that carry out different functions work together to from an organ. Different organs that carries out different functions work together to from a system. An differnt systems that carry out different functions work together to from an organism! That is LIFE :D
Different cells of the same type work together to form tissues. Different tissues that carry out different functions work together to from an organ. Different organs that carries out different functions work together to from a system. An differnt systems that carry out different functions work together to from an organism! That is LIFE :D
EVEN PLANTS HAVE ORGANS!!!!
Examples of plant organs are:
Flowers, roots, leaves, stems.
Microscopes
Just because u can see something, doesnt mean its not there!!! A microscope allows us to see things that cannot be seen with the naked eye, such as cells and bacteria.
This is a basic stero light microscope.This is a electron microscope, capable of magnifying 1000,000x!
This concludes what i have learnt so far for term 2-3!!!